Home Security - Lesson 1: Guide to Selecting a Home Security Camera
Choosing a home security camera system can be overwhelming due to the wide range of options, features, and technical considerations. This guide outlines the top 12 factors to consider when selecting the right security cameras for your home.
1. Wired vs. Wi-Fi Security Cameras
When selecting a camera system, the first decision is whether to go with a wired or Wi-Fi-based system.
Wired Systems (NVR/DVR)
Use a hardwired connection for both power and data transmission.
Typically support multiple cameras (4, 8, or 16 cameras) in a centralized system.
More reliable because they are not dependent on Wi-Fi signal strength.
Best for: Comprehensive outdoor coverage, high-security applications.
Wi-Fi Cameras
Connect to the home’s wireless network and offer more flexible placement.
Can be standalone or part of a multi-camera setup.
Best for: Indoor monitoring, small-scale surveillance, or areas where running wires is impractical.
Key Consideration:
If the goal is complete perimeter security, a wired system is recommended. If only a few cameras are needed indoors or in smaller spaces, Wi-Fi cameras may be more suitable.
2. Power Options
Understanding how security cameras receive power is critical:
Wi-Fi Cameras:
Plug-in Power: Reliable but requires access to an electrical outlet.
Battery-Powered: Offers flexible placement but requires recharging.
Solar-Powered: Extends battery life but requires sufficient sunlight.
Wired Systems (PoE - Power over Ethernet):
Receives both power and data through a single CAT5/CAT6 cable connected to an NVR (Network Video Recorder).
Provides continuous power and recording without reliance on batteries.
Typically requires running network cables from a central hub to each camera location.
Key Consideration:
If frequent battery recharging is a concern, PoE-powered cameras or solar-assisted Wi-Fi cameras can be a more sustainable option. If you are seeking a 24/7 monitored system (like SimpliSafe or other professional monitoring services), plan for constant power at each camera location, which may require additional electrical work during installation.
3. Price vs. Quality
Security cameras range widely in cost based on features, durability, and recording quality.
Lower-cost cameras often have lower resolution, shorter lifespan, and fewer advanced features.
Higher-end cameras provide better durability, clearer resolution, and more advanced security features such as AI detection, night vision, and cloud integration.
Key Consideration:
Investing in reputable brands ensures reliability. Avoid unknown brands with no track record of software updates or security patches.
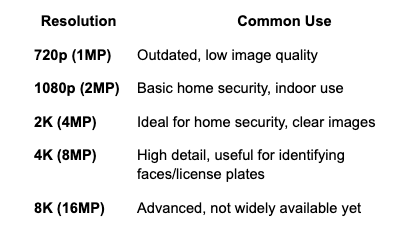
4. Resolution & Video Quality
Security cameras are available in different resolutions:
For most residential applications, 2K resolution is the optimal balance between quality and storage efficiency.
4K resolution is best for large properties where zooming in on footage is necessary.
5. Night Vision Capabilities
Cameras should provide clear footage in low-light conditions.
Infrared (IR) Night Vision: Displays images in black & white and uses IR LEDs to illuminate the scene.
Color Night Vision: Uses a built-in spotlight or ambient light sources to maintain color footage at night.
Key Consideration:
Infrared is common, but color night vision provides more detailed footage and is beneficial for identifying objects or clothing colors.
6. Camera Placement & Coverage
Strategic camera placement ensures complete coverage. Key locations include:
✅ Main entry points (front & back doors, garage doors)
✅ Driveways and walkways
✅ Backyard and side yard access points
✅ Windows that are potential entry points
✅ Interior areas (main living spaces, hallways, nurseries)
For outdoor placement, consider weatherproof and vandal-resistant designs.
7. Stationary vs. PTZ (Pan-Tilt-Zoom) Cameras
Stationary Cameras:
Fixed position, continuously monitors one area.
Recommended for covering entry points, driveways, and perimeters.
PTZ (Pan-Tilt-Zoom) Cameras:
Can remotely adjust viewing angles and zoom to follow movement.
Best for monitoring large open areas or tracking movement in real-time.
Key Consideration:
PTZ cameras can be useful for active monitoring, but stationary cameras ensure continuous coverage of key areas without manual adjustments.
8. Audio Capabilities
No Audio: Some cameras only record video.
One-Way Audio: Captures sound from the environment but does not allow interaction.
Two-Way Audio: Allows communication through the camera (useful for deterring intruders).
Key Consideration:
If using cameras for home security or delivery monitoring, two-way audio can be an effective deterrent.
9. Viewing & Access Options
Monitor/TV Viewing: Direct connection to a dedicated screen.
Smartphone & Tablet Apps: Allows remote viewing through manufacturer apps.
Cloud Access: Enables playback from any location with an internet connection.
Key Consideration:
Ensure that the camera system offers remote access options and is compatible with mobile devices or smart home integrations.
10. Video Storage Options
Choosing the right video storage method is critical for retaining security footage. Storage solutions fall into two main categories: local and cloud-based storage.
A. Local Storage (No Monthly Fees)
✅ Network Video Recorder (NVR) / Digital Video Recorder (DVR)
Records 24/7 on a built-in hard drive.
Storage capacity varies (1TB–8TB standard, expandable).
Best for: Wired camera systems, no subscription fees.
✅ MicroSD Cards (Individual Cameras)
Each camera stores its own footage on an SD card.
Typically supports event-based recording, not continuous recording.
Best for: Standalone Wi-Fi cameras with no cloud fees.
✅ Network Attached Storage (NAS)
Centralized local backup solution for multiple cameras.
Best for: Large-scale security setups with data redundancy.
B. Cloud Storage (Monthly Fees Apply Per Camera or Plan)
Some security camera brands require a paid cloud subscription for storing and accessing recorded footage. These services typically charge per camera or offer multi-camera plans.
C. Hybrid Storage (Local + Cloud Backup)
Some brands, like Lorex and Eufy, allow for both local and cloud storage, giving users more control over their data.
✅ Best for: Users who want cloud backup but don’t want to rely on it exclusively.
Key Considerations When Choosing Storage:
✔ If you prefer no fees: Choose NVR/DVR systems or MicroSD-based cameras.
✔ If you want easy access from anywhere: Consider cloud-based storage.
✔ If you need 24/7 recording: NVR/DVRs or Nest Aware Plus (for CVR) are the best options.
NOTE: The Hidden Risks of Internet-Connected Security Cameras
While internet-connected security cameras offer convenience and remote access, they also introduce significant privacy and security vulnerabilities. Understanding these risks is crucial for safeguarding your home and personal information.
Real-World Incidents of Camera Hacking
Verkada Breach (2021): Hackers gained access to over 150,000 live security camera feeds from various organizations, including hospitals, schools, and private residences. They exploited administrative credentials found online, highlighting the dangers of centralized cloud-based systems.
Ring Camera Intrusions: In multiple instances, unauthorized individuals accessed Ring cameras inside homes, speaking to occupants and even children. These breaches were often due to compromised user credentials, emphasizing the need for strong, unique passwords and two-factor authentication.
TRENDnet Vulnerability: A flaw in TRENDnet's IP cameras allowed live feeds to be accessed without a password, exposing private activities within homes. The FTC took action against the company for failing to secure their devices adequately.
Why Standalone Systems Offer Enhanced Security
Standalone security systems operate independently of the internet, reducing exposure to remote hacking attempts. Benefits include:
Local Data Storage: Footage is stored on local devices, eliminating risks associated with cloud storage breaches.
Reduced Attack Surface: Without internet connectivity, these systems are less susceptible to remote exploitation.
Enhanced Privacy: Data remains within your control, minimizing the chances of unauthorized access or surveillance.
Protecting Your Home Security System
If you use internet-connected cameras:
Regularly Update Firmware: Manufacturers release updates to patch security vulnerabilities.
Use Strong, Unique Passwords: Avoid default credentials and consider using a password manager.
Enable Two-Factor Authentication: Adds an extra layer of security beyond just a password.
Limit Sharing: Be cautious about who has access to your camera feeds and avoid sharing login information.
For those prioritizing privacy and security, investing in a standalone system may be a prudent choice.
11. Understanding What is being Recorded
It's important to understand a few features that can enhance both the functionality and effectiveness of your security setup.
A. Viewing vs. Detection Range
○ The viewing range refers to the maximum distance at which the camera can capture clear, detailed images.
○ The detection range is the area within which the camera’s motion sensors or analytics can detect movement and trigger a recording or alert.
○ Key Consideration: The detection range may be shorter than the viewing range, so ensure the sensor covers the area you need to monitor.
B. Recording Length and Retrigger Time
○ Recording length denotes the duration of video captured during a single recording session, whether it is continuous or event-triggered.
○ Retrigger time is the minimum interval that must pass after a motion-triggered recording before the camera will begin recording again.
○ Key Consideration: Setting an appropriate recording length and retrigger time helps capture complete events without creating excessive redundant footage, thus optimizing storage.
C. Live View vs. Saved Footage
○ Live view provides a real-time video feed that can be accessed via a smartphone, tablet, or computer, allowing immediate monitoring.
○ Saved footage refers to the recorded videos that are stored locally (e.g., on an SD card or DVR/NVR) or in the cloud for later review.
○ Key Consideration: Live view is ideal for immediate response, while saved footage is crucial for reviewing past events or providing evidence in the event of an incident.
12. Smart Home Integration
Security cameras can integrate with smart home systems, such as:
✅ Amazon Alexa & Google Assistant (voice control)
✅ Apple HomeKit (secure smart home automation)
✅ Smart locks, lights, and alarms for enhanced security automation
Key Consideration:
If home automation is a priority, choose cameras that support integration with your existing smart home devices.
Final Thoughts
Selecting the right home security camera system depends on your specific needs, home layout, and security concerns.
✔ Wired systems are best for outdoor and high-security setups.
✔ Wi-Fi cameras offer flexibility and easy installation.
✔ Consider resolution, night vision, and storage options carefully.
✔ Strategic placement enhances effectiveness.
By considering these factors, you can build a security system that provides peace of mind and reliable home protection.